
Customer Data Hub
Organizations are increasingly striving to improve the customer experience to create differentiation for their brand/service in the customers' minds. Also, customers demand the flexibility to interact with a brand…
Organizations are increasingly striving to improve the customer experience to create differentiation for their brand/service in the customers’ minds. Also, customers demand the flexibility to interact with a brand through the channel of their choice (Web, Mobile, Email, Call, etc.). One crucial aspect of creating a superior customer experience is providing them this flexibility and ensuring a seamless experience irrespective of the channel. To do this, you need to know your customer well – their demographics, interests, preferences, interaction histories, etc. A Customer Data Platform (CDP) can help the organization create that single repository of enriched customer profiles and their activities.
The CDP pulls the data from diverse transaction systems and applications (both online and Offline) to stitch together a comprehensive 360-degree view. The main objective here is to perform the data integration, cleansing, and matching of customer data only once and then use this enhanced customer data for all the reporting and decision-making applications. This ensures that enriched customer profiles are readily available for decision-making and reduces the duplication of effort.
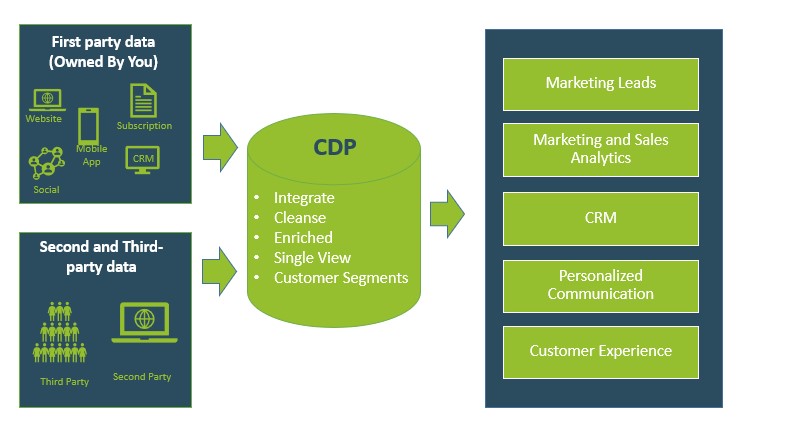
What data is collected for CDP:
In general, any data related to a customer can go in a CDP. More specifically, the following data is often loaded:
Prospect/ Customer AttributesThis includes the customer demographic and contact-related details such as name, address, gender, age, IP address, type of device used, etc. This data can be predominantly categorized as first party, second party, and third party data
First-Party Data
The first-Party customer data is the data collected directly from the customer’s activities on the website, such as browsing pages, scrolling, clicking, etc. It also includes emails, addresses collected via forms or subscriptions.
Second-Party Data
At times, the first-party data available with you may be limited and can thus hamper your attempt to reach a wider audience. In such cases, companies could opt to buy second-party data. Second Party data is nothing but someone else’s first-party data. A company other than yours might collect valuable contact and other details about their users and may be willing to share it with you at a price. E.g., A company providing services to buy/sell used cars may sell their data to a finance company or insurance company about people interested in buying cars, or people who own specific models, or people who need car financing, etc.
Third-party Data
Third-party data is data that companies buy from outside sources, typically aggregators, that are not the first authorities of that data. Third-party data is mainly collected from data providers to create new customer segments or enrich the existing ones and use it to initiate marketing campaigns for customer acquisition or other such initiatives. There are marketplaces available such as Lotame PDX, LiveRamp, Audience Prime, etc., which facilitate buying and selling this type of data.
Customer Behaviour
This is the behavioral data such as the user’s activities during a website or mobile application, or the user’s behavior on social media such as likes on a post, sharing of content, clicks on links, etc.
Features
Purchase History
Data related to eCommerce activities, sales systems that generate purchase bills, orders and renewals, abandoned carts, etc., is collected to boost sales, discover vulnerabilities, and develop new insights useful in marketing activities.
Campaign performance data
This is the data on marketing communication sent to customers and their response to these campaigns, such as clicks, impressions, views, etc.
Customer Service
This includes customer interaction data such as live chat data, call-center data, frequency and duration of interaction, etc.
What processing is done in CDP to enrich customer data?
The data collected using the CDP platform can be processed and manipulated to serve the downstream analytics and applications. The processing done on the raw data pulled from multiple systems depends on the application being deployed or analytics being leveraged on CDP and can also vary from platform to platform. Mentioned below are some bare minimum cleansing and integration activities, the result of which can be leveraged by multiple systems and applications:
Entity Resolution or Customer 360
Entity resolution essentially consists of creating linkages between multiple customer transactions. This can be done by matching cookies across sessions or can involve a more probabilistic approach of matching customer transactions based on the combination of attributes such as name, email id, contact number, Facebook id, cookies, etc. The result is the unique tagging/grouping of every transaction to a known customer or an unknown prospect.
Customer Journey
Customer journey is a sequence of user activities related to the customer’s interaction with the business through multiple channels. This can be a sequence of actions by the user on the website or his interaction with the call center or his visits to a physical store, etc. a CDP can store pre-stitched journeys which can be used across multiple applications.
Why CDP/Application
Improved efficiency
Data handling is one of the significant issues that many organizations face when setting up new technologies or feeding data to existing models. CDP centralizes data, saving hours of integration work, and removes redundancies to improve the operational efficiency with no duplicate record in the system.
Enhanced quality of customer data
Low-quality data results from multiple applications, systems, and process limitations in collecting data. It can also be due to data-entry issues or natural data challenges such as multiple emails, phone numbers, alternate customer names/spellings, etc. A CDP attempts to overcome the inconsistencies, fill in any missing information, clean records, remove duplicates, and create an enhanced 360-degree view of the customer.
Democratization of customer data
Multiple departments such as sales, customer support, marketing, etc increasingly rely on integrated customer data to drive efficient operations. CDP democratizes this customer data and makes it accessible to all the departments and users without having to get into the technical nitty-gritty of integration and cleansing.
Ready customer segments
Often CDP also keeps pre-segmented data. The segmentation is typically based on demographics, customer transactions, preferences, etc. Multiple departments can then use these readily segmented data for targeting through marketing campaigns, offering a promotion, or maintaining/improving the quality of customer service, etc.
How is CDP different than other similar customer data repositories?
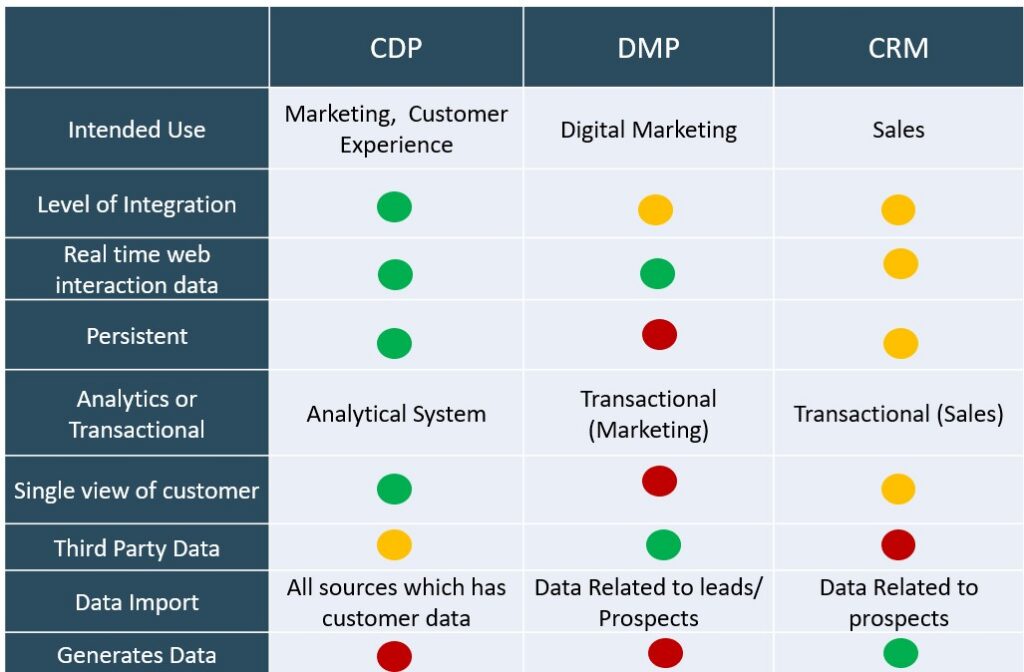
While CDP, DMP- Data Management Platform, and CRM- Customer relationship Management all seem to have customer data, each of them has a distinct purpose. The level of details offered by each of them may also differ. Here is a comparison between CDP and other similar customer data repositories to give clarity to our readers.
Difference between CDP and DMP
- The primary objective of creating a DMPs is to execute digital marketing. Unlike CDP, DMP does not focus on persistent customer profile and integrations
- Besides customer attributes, CDP also has data about customers’ purchase histories and service interactions, whereas DMP mainly focuses on customer attributes and contact information.
- CDP mainly focuses on the first-party data, but it can also be enriched using second and third-party data, while DMP focuses on the first- and third-party data to allow for a broader reach in digital marketing
- CDP is used to maintain a customer profile for longer-term, while DMP is used for a shorter term.
Difference between CDP and CRM systems
- The primary objective of CRM is to manage customer transactions such as sales, customer support, etc. In contrast, a CDP acts as an integrated customer data repository to support marketing and customer Analytics (Although this differentiation is increasingly blurring out).
- CRM is a transactional Application used to capture the customer’s details during the sales process, whereas CDP is an analytical repository for marketing purposes to target audiences and increase sales.
- CRM data can provide you with a client’s name, history of transactions with the business organization, complaints they have filed, etc. CDP data can give the customer interaction journey from first to other clicks to subsequent visits and purchases.
- A CRM may not support real-time marketing, CDP on the other hand, can get real-time customer behavior data and make it available for real-time analytics.
The chart below can give you a fair idea about some of the subtle differences. Please note that this is only meant to provide you with an idea and may vary from solution to solution.
Applications of CDP:
We have so far discussed the data and system advantages of using a CDP platform to get a complete profile/picture of the customer and their behavior. The organization can use this detailed view to achieve higher goals such as :
Improve Sales
The customer details and preferences in CDP can be leveraged to understand customer inclinations and readiness to buy a product or a service. Using this information a customer can be targeted with a more impactful offer leading to improved conversion.
Drive Effective Marketing
A CDP stores the point-in-time journey of customers. This journey can be used to trigger certain marketing activities such as sending a reminder on the abandoned cart, sharing brochures to improve awareness, sending a promotional offer to increase conversions, etc.
Customer Segments provided by CDP can also be leveraged to work out the probability of churn. The customer segments with high churn probability e.g., can be offered incentives to prevent churn.
Enhance Customer Experience
Customers’ ready information, preferences and likes/dislikes, historical purchases, and other transactions can be leveraged by customer service teams for prompt and proactive resolutions leading to superior customer experience.
You Might Be Interested In

Unleashing the Power of Large Language Models
In today's digital age, Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to push the boundaries of what's possible, and one area that's capturing widespread attention is Large Language Models (LLMs). These sophisticated AI…

Death of Third Party Cookie Part 1
By now, all the marketers are aware of Google's plan to phase out third-party cookies in Chrome. It's not too far. By the end of 2023, the third-party cookie will…

Marketing Automation
Organizations with a sizable inflow of users on their website or mobile application grapple with the task of managing these leads for effective conversion. Users looking at your products/services may…


